Projekte
Publikationen
Forschungsthemen
Unsere Gruppe beschäftigt sich in der Forschung mit Fragen der Web-Technologie sowie mit Netzwerken und damit verbundenen Aspekten der Sicherheit und Privatheit.
Im Bereich Web-Technologie interessiert uns, wie Informationen am besten zum Endanwender transportiert werden. Dabei konzentrieren wir uns insbesondere auf die Anwendungssituation im Unterricht und in der Sitzungsunterstützung, da wir die entsprechenden Anforderungen aus eigener Anschauung am besten kennen und bei uns ein geeignetes Testumfeld vorfinden. Wir haben eigene Systeme entwickelt und erprobt, die unter anderem im Startup-Unternehmen Tweedback vertrieben werden. Weitere Fragen beschäftigen sich mit der Informationsdarstellung für den Wissensarbeiter auf mobilen Endgeräten.
Im Bereich Sicherheit von Netzwerkn beschäftigen wir uns z.B. mit Reverse Engineering von Netzwerkgeräten, Feldbussen und deren Sicherheit. Der Fokus liegt auf den Gebieten Gebäudeautomation, Industrielle Automation / Operational Technology und Feldbussen in Fahrzeugen.
Aktuelle Projekte
2023-2026 - DiSH-O-Klin - Digitale Stimulation von Hygiene- und Optimierungsmaßnahmen für den Klinikbetrieb
Ziel des Projektes DiSH-O-Klin ist die Entwicklung und Bereitstellung eines umfassenden digitalen Anreiz- und Dokumentationssystems zur Optimierung der Hygienesituation im Klinikbetrieb.
Hygiene und speziell Händehygiene entsprechend den WHO-Indikationen ist in medizinischen Einrichtungen die effizienteste bekannte Maßnahme, um Infektionsübertragungen zu reduzieren. In "DiSH-O-Klin" wird ein digital vernetztes elektronisches System zur permanenten Vermessung und Regelung der Hygienesituation entwickelt, pilotiert und als demonstrierbare Referenzlösung zur Verfügung gestellt. Vor dem Hintergrund zunehmend vorkommender multiresistenter Erreger und globaler Ausbreitung neuer Infektionskrankheiten gewinnt die Vermeidung von Infektionen und Erkrankungen durch Hygiene zunehmend an Bedeutung.
Die Entwicklung eines gesamtheitlichen digitalen Verständnisses zum Thema Hygiene und Infektionsvermeidung in Kliniken und die daraus resultierende selektive und individuelle Stimulierung der Durchführung von Händehygiene, Anpassung organisatorischer Abläufe, risikobezogene Infektionstests ist Ziel des nachfolgend beschriebenen Vorhabens.
Mitarbeiter: Frank Russow
Projektleiter: Thomas Mundt
2023-2025 - OSSIS – Entwicklung eines innovativen On-Ship Sicherheit-Informations-Systems für Operations Technology
Der Fokus dieses Projekts liegt auf der Sicherheit von Feldbussen in der Operational Technology des Schiffes. Die Universität Rostock übernimmt die Entwicklung von Algorithmen für die Analytik der Datenströme in den Protokollen. Es wird angestrebt, eine Hardwareplattform zu entwickeln, auf der die Analytik der Datenströme und der Funktionen realisiert werden. Von der Universität werden die Algorithmen für Erkennung von Anomalien in den Feldbussen aufgrund Manipulationen und Fehlfunktionen entwickelt. Auf Grundlage der Zusammenarbeit mit den Partnern aus dem nautischen Bereich werden auch Algorithmen entwickelt, die in der Lage sind, abweichendes Schiffsverhalten zu erkennen bzw. in den Datenströmen der schiffsinternen Feldbusse zu detektieren. Um die Analysealgorithmen zu optimieren wird auch eine Untersuchung von unbekannten Datenpunkten (z.B. nicht vom Hersteller offen gelegte Schnittstellen) erfolgen, wobei es auch notwendig werden kann, aus Sicherheitsgesichtspunkten unbekannte Protokolle zu evaluieren.
Mitarbeiter: Marvin Davieds
Projektleiter: Thomas Mundt
2022-2024 - GES2021 - Gebäudesicherheit
In den zurückliegenden Jahren wurden in enger Zusammenarbeit zwischen dem Institut für Informatik, Lehrstuhl für Informations- und Kommunikationsdienste (IuK) und dem Dezernat Technik, Bau, Liegenschaften zahlreiche Sicherheitsanalysen in der Gebäude- automation der Universität Rostock durchgeführt und zahlreiche Defizite festgestellt. Diese Defizite betreffen die gesamte Gebäudeautomations-Struktur (Management-, Automations- und Feldebene), die Organisationsstruktur, die Bau- und Errichterebene (Bauherren), sowie die Gesetzesvorlagen für Baumaßnahmen im Land M-V.
In diesem Projekt werden genau diese Defizite tiefgreifend analysiert, Schwachstellen benannt und in Lösungsansätze überführt, sowie Maßnahmen erarbeitet, die ein standardisiertes Vorgehen in Bezug auf die gebäudesichert ermöglichen. Weiterhin werden sogenannte Penetrationstests durchgeführt, um das Ausmaß unserer Datenstrukturen zu erkennen. Das Ziel ist die Sicherheit in der Gebäudeautomation zu erhöhen, vor externen und internen Fremdzugriffen zu schützen und somit einen sicheren Betrieb zu gewährleisten.
Mitarbeiter: Jan Heisenberg
Ehemaliger Mitarbeiter: Marvin Davieds
Projektleiter: Thomas Mundt
Auftraggeber: Universität Rostock, Dezernat für Bau und Liegenschaften (D3) - Ansprechpartner: Peter Wickboldt
Nicht mehr geförderte Projekte
SeThi - Summer School on Security in the Internet of Things
BloSSom - Blockchain and Smart Contracts Summer School
BaSoTI - Baltic Summer School Technical Informatics and Information Technology
ISAR - Interdisziplinäre Sommerakademie Rostock
TopoTool - Entwicklung eines Werkzeugs zum Mapping von Feldbus-Infrastrukturen
Feldbusse vernetzen Sensoren und Aktoren in Automatisierungssystemen. Bedingt durch die lange Lebensdauer der Systeme und oftmals unzureichende Dokumentation von Veränderungen ist es während der Lebensdauer kaum möglich, eine aktuelle Übersicht über die vorhandene Infrastruktur zu erhalten. Damit werden aber auch Bedrohungsanalysen und die Ergreifung von Gegenmaßnahmen massiv erschwert. Schwachpunkte in den Installationen bleiben unerkannt. Durch mangelnde oder unvollständige Dokumentation mit Medienbrüchen wird eine Übersicht zusätzlich erschwert. Erfahrungen zeigen, dass selbst unmittelbar nach Errichtung und Übergabe einer Industrieanlage oder eines Gebäudes mit Feldbussen die Dokumentenerosion kritische Zustände erreicht. Praktisch ist kein Netzwerk in dem Zustand, in dem es geplant wurde bzw. der dem Dokumentationsstand entspricht.
Eine vollständige Bestandsaufnahme und Bedrohungsanalyse ist heute mit erheblichem personellen Aufwand verbunden. Diese Kosten möchten viele Anwender vermeiden und in der Praxis wird oftmals erst nach einem Schadensfall eine – teilweise nur punktuelle – Analyse durchgeführt. Mit dem vorgeschlagenen Projekt soll hier ein Lösungsansatz angeboten werden. Es soll ein System entwickelt werden, das auf Basis vorhandener analoger und digitaler Datenquellen ein Abbild der aktuellen Infrastruktur aufzeigt. Weiterhin soll auf dieser Grundlage eine automatisierte Erkennung von Schwachpunkten und möglichen Angriffsszenarien erstellt werden.
TopoTool ist Teil des größeren SIINDUS-Netzwerks und wird vom Bundesministerium für Wirtschaft und Energie über das ZIM-Programm (Zentrales Innovationsprogramm für kleine und mittlere Unternehmen) gefördert.
Kontaktieren Sie Darshit Pandya oder Thomas Mundt für weitere Informationen.
SeBuNet - Lösungen für sichere Feldbusse auf dem Physical Layer
Die bei Feldbussen eingesetzten Protokolle müssen im Wesentlichen ohne besondere Sicherheitsfunktionen auskommen. Durch unbefugtes und unbemerktes Eindringen ins Netzwerk ist möglich, die Konfigurationen der verschiedenen angeschlossenen Geräte zu ändern oder auf den Auslieferungszustand zurückzusetzen. Für diese Szenarien benötigt der Angreifer direkten Zugriff auf das Netzwerk. Auf Grund des Aufbaus von Feldbussen ist es allerdings in der Regel möglich, sich an fast jedem Punkt an „einen Draht“ zu hängen. Mit einfachen technischen Mitteln ist eine Abhör- und Angriffseinrichtung zu realisieren. Der Zugang zu einer geeigneten Dose oder Kabelstrang ist – gerade in öffentlichen Gebäuden – einfach.
Somit erscheint es sinnvoll und notwendig, diese Netzinfrastrukturen auf der Feld-Ebene in der Gebäudeautomation abzusichern. An dieser Stelle soll die geplante Lösung des Vorhabens ansetzen. Es ist das Ziel der Partner des Vorhabens „SeBuNet“, ein System zur internen Überwachung von Feldbus-Netzwerken zu entwickeln. Das System soll in der Lage sein, potentielle Angriffe auf das Netzwerk bereits beim Aufschalten auf das Netzwerk, zu erkennen.
Die Idee besteht in der Entwicklung einer zusätzlichen Netzkomponente, die den Bus passiv überwacht und Anomalien erkennt. Dies ist beispielsweise der Fall, wenn zusätzliche Geräte an den Bus angeschlossen werden oder vorhandene Geräte entfernt oder versetzt werden. Mit Hilfe der zu entwickelnden Netzkomponente ist es möglich, diese Veränderungen am Bus zu erkennen, die mit Hilfe konventioneller Paketanalyse nicht erkannt werden können.
SeBuNet ist Teil des größeren SIINDUS-Netzwerks und wird vom Bundesministerium für Wirtschaft und Energie über das ZIM-Programm (Zentrales Innovationsprogramm für kleine und mittlere Unternehmen) gefördert.
Kontaktieren Sie Andreas Zdziarstek oder Thomas Mundt für weitere Informationen.
EMERGE IoT - Entwicklung von Kompetenzen, Methoden und Werkzeugen für zukunftsorientierte Ermittlungen und Ermittlungsunterstützung im Internet der Dinge
EMERGE-IoT steht für Entwicklung von Kompetenzen, Methoden und Werkzeugen für zukunftsorientierte Ermittlungen und Ermittlungsunterstützung im „Internet of Things“. Das Projekt wird von 2018-2021 mit Mitteln des Europäischen Fonds für die Innere Sicherheit – ISF gefördert und läuft in Zusammenarbeit mit dem Landeskriminalamt Mecklenburg-Vorpommern.
Unsere Ziele
- Identifizierung und Analyse der technischen Grundlagen des IoT
- Entwicklung und Überprüfung von polizeilich relevanten IoT-Angriffsszenarien
- Entwicklung von Werkzeugen zum Erkennen und Analysieren von Angriffen
- Vermittlung von Wissen zum Phänomen IoT an die Strafverfolgungsbehörden
Zu weiteren Informationen besuchen Sie bitte die Projektwebseite oder wenden Sie sich an Johann Bauer oder Thomas Mundt.
SINDABUS - Security Components for Industrial Automation and Fieldbus Systems
The SINDABUS project aimed to improve the security of IT infrastructure found in industrial automation and field bus systems.
The Consortium, consisting of the University Rostock together with two corporations SKM Informatik and Logic Way, developed individual moduls that put together a construction kit to enhance the cyber security of thos systems. The results helped to enhance protection of heterogeneous network infrastructures within production plants and building automation systems - across protocol boundaries - against malicious attacks from the inside as well as from the outside.
SINDABUS was part of the greater SIINDUS network and was funded by the German Federal Ministry of Economics and Energy via the ZIM program (Central Innovation Programme for Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises).
VestiFi
VestiFi is a startup that helps to solve WLAN problems in corporate environments. The service offered by VestiFi is based on an innovative device which was developed as part of a PhD thesis at the Department of Information and Communication Services, University of Rostock. Companies that are interested in the service please contact Christoph Müller by e-mail () or telephone (0381 498 7507) for further information.
As of 2016, the startup is funded by an EXIST Business Start-up Grant from the German Federal Ministry of Economics and Technology (BMWi) and co-financed by the European Social Fund (ESF).
WaveHopper
The cooperative research project WaveHopper was awarded a grant funded by the Mecklenburg-Vorpommern ministry for economic development. In cooperation with Logic Way GmbH from Schwerin we investigate possibilities to deliver network traffic in a hop-by-hop manner from harvesting machines on a farm to food processing facilities.
Technologically, this implies researching radio transmission protocols on different layers, delay tolerant routing schemes, and hardware design. The project originated from the networking project “hisfood.net”. The project started in early 2014 and is estimated to run one year.
Tweedback
Tweedback is an innovative project which aims to improve communication and feedback in lessons with large audiences. Forms of feedback that work perfectly in seminars, as teachers want to proof the level of understanding for example, are not applicable in large lessons. At this point Tweedback provides a solution.
Tweedback is partly funded by BMBF and the Institute of Computer Science, University of Rostock. More information in German language can be found on the Tweedback website.
Multiscript
The project multiscript offers students the possibility to make annotations and remarks into the lecture materials of the docent. The student can share the remarks with other students as well as with the docent. The goal is to let the lecturer see where students have problems with understanding and to engage the students, even across cohorts, in a debate about the topic they want to learn. From a pedagogic point of view the student is actively working, commenting and restructuring material and discussing comments with colleagues–which leads to a better overall learning effect than solitary learning.
Authenticated Positioning
This projects researches methods to proof someone's position over a network connection. The entire process from position determination to location dependent rights management is studied.
Project Details “Authenticated Positioning”
This internal project researches possibilities to provide location information in an authenticated way. This means, for instance, a position information can be transmitted via e-mail and the receiver will be able to determine whether the provided information is trustworthy.
Aspects under research are methods to determine a subject's position, trust in position information, transport of authenticated position information, and applications.
Applications are entertainment systems (limiting broadcasts to certain areas) and protection of sensitive materials.
Content Lecture Interface
In this project, we aim to improve the process of content delivery in a lecture. We provide an interface for the audience to interact with taught content during a lecture. Using the information from these interactions we enrich current slide shows with crowd sourced semantic information. These information help the individual of the audience to identify issues in comprehension and the lecturer to get a feedback on overall comprehension. Furthermore, information are used to enable topic and issue based discussions after a lecture. The final step aims for automatic assistance during a lecture based on individual needs and available semantical enhanced lecture material.
This work is supported by the German Research Foundation (DFG) as part of the research training group MuSAMA (grant no. GRK 1424/1).
Online Social Networks for the Blind
This PhD research project aims to improve the accessibility and usability of Online Social Networks. These networks are an example of highly complex websites with as much information as possible on one single page in order to find the desired information with as few clicks as possible. Due to the complexity, such websites are difficult to access for blind users surfing the web with a screen reader.
If provided, blind users often rely on the mobile website, since its structure usually is clear, simple and straightforward and consequently easier to access for a screen reader. However, mobile websites often do not offer the same amount of information and functionalities as the corresponding regular website does. Therefore, when using the mobile website only, users are excluded from certain information and functionalities.
To improve the accessibility and usability of Online Social Networks by providing a user centered solution, first a structural equation model will be developed to explain the differences in the intention to use as well as in the actual use of Online Social Networks between sighted and blind users. Those differences then lead to design recommendetions for web developers to make Online Social Networks more accessible and usable for blind users.
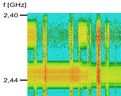
Measurement and Prediction of Channel Occupancy in IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN
The PhD research project is focussed on measuring and predicting the usage intensity of wireless channels in the 2.4 GHz ISM band in conjunction with IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN. The goal is to give each WLAN device the possibility to avoid channels with high near-term channel occupancy and to adjust services and protocols according to the expectable network quality. In order to allow a wide-spread application, measurement systems are investigated that can be implemented in off-the-shelf WLAN devices with low additional cost. As part of the thesis, extensive measurements have been carried out to assess channel occupancy patterns and wireless devices' behavior.
This work is supported by the German Research Foundation (DFG) as part of the research training group MuSAMA (grant no. GRK 1424/1).
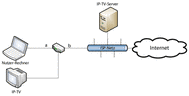
Neutrality and Transparency of Networks and Applications
Over the last couple of years, network neutrality has become an interesting research topic. Typically, questions regarding different handling of data packets during their transport are discussed. The issue of network neutrality usually leads to binary answers. Either a network is neutral – or not: There are no nuances of network neutrality. In a world in which network applications relying on a certain level of network quality (e.g. television over Internet (IPTV) or voice over IP (VoIP)) are available to the public, those definitions hardly comply with reality. Not the knowledge, whether a network is neutral but the knowledge which measures are applied to traffic should be considered.
This work was support by a two-year scholarship of Landesgraduiertenförderung Mecklenburg-Vorpommern.
Social Implications of Digitally Structured Spaces
Social Implications of Digitally Sctructured Spaces
The increasing digitalization of social life, defined as a relocation of social action from the “primordial” environment of men into digital space, indicates radical changes of the social itself. It is presumed that the distinct constitutions of analogue and digital space cause profound changes in the social life of human beings. These changes are not (exclusively) the result of obvious, „superficial“ phenomena of the digital world, such as space-time-compression, multioptionality, changes in temporal structures or permanent availability, but rather the direct, basic consequence of the digitality of the new environment itself. It is assumed that it is the basic structure of the digital space which leads to massive changes of sociality and society. Some of these consequences, as symptoms of the underlying process of digitization itself, are already visible today because of their efficacy: The possibility of comprehensive detection (and therefore surveillance) of digital human action, the increasing use of algorithms to solve problems or the rise of automated decisions, that do not depend upon human beings. The main objective of this dissertation project is the disclosure of the genuinely different structures of analogue and digital environment. The significant differences in the constitution of analogue and digital space will not only be elaborated in a descriptive way, on an abstract and theoretical level, but also on the basis of current „symptoms“ such as the comprehensive monitoring of human action or the increasing importance of algorithms in the context of automated evaluation of human action and the resulting shift of power of interpretation away from human beings towards algorithms.
Robert Brumme is fellow of the graduate school "Deutungsmacht" funded by the DFG and scholarship holder of the "Landesgraduiertenförderung". He studies the social implications of digitally sctructured spaces. Prof. Peter A. Berger and Prof. Clemens H. Cap are his supervisors
Digital Surveillance
Referring to latest revelations, disclosed by the former NSA-Member Edward Snowden, Surveillance has become a buzzword in general public and one of the main topics in politics of western democratic countries. In oder to cope with these political challenges concerning the individual liberty, which are caused by social change and technical progress, there is an ever-extending need for academic examination of Surveillance and its consequences for Modern Society.
To reclaim the contemporary issue within an interdisciplinary and structured manner, we collaborate with the Department Knowledge–Culture–Transformation, one of the four profiling fields of the Faculty of Interdisciplinary Research.
In this context research assistant Christin Schumacher works on the junction of multidisciplinary expertise based on current sociological discussion and informatic research on the technical conditions and opportunities of Digital Surveillance.
Privacy and Security in Building Automation Networks
Intelligent buildings require networks that interconnect sensors, actuators, controllers, and management systems. Fundamental security and privacy aspects that have been developed for computer networks are not commonly established and accepted for building automation networks. We provide research to help overcoming this unsatisfying situation. Please contact Thomas Mundt for further information